
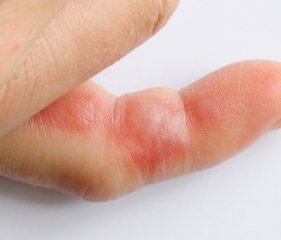
 Wasp stings can be very painful and for some people even potentially life threatening.
Wasp stings can be very painful and for some people even potentially life threatening.
There is no anti-venom available for wasp or hornet stings but most stings can be handled using simple first aid techniques. If you develop an allergic reaction to the sting you should seek immediate medical attention as you will require medication to help counter the effects.
All wasps are different. There are various species including the yellow jacket and the paper wasp. More interestingly you will never get stung by a male wasp. It is a pity we can’t tell the difference at first sight but only females sting. The first action to be taken following a wasp sting is to remove “the stinger” from the body. This is best done with a pair of tweezers or scraped out with the fingernail. There will probably be a desire to rub and squeeze the affected area in order to reduce the pain as this gives the impression that the pain is reduced. However, our specialists recommend not doing this as it will cause the venom to spread beneath the skin.
After cleaning the affected area place something cold like ice cubes or an ice pack over the area (wrapped in something like a towel). In order to reduce swelling rest and possibly elevate the affected area. For extra protection – especially if the patient is itching a lot – an antihistamine or oral tablet can be useful. Over a couple of days the symptoms should subside but if after two days it appears the swelling and redness is spreading over a wider area this is a sign the patient may have an infection and it is recommended medical advice should be sought.
 The most important first step is to remove the sting as quickly as possible. You need to be very careful not to break the sting whilst removing it.
The most important first step is to remove the sting as quickly as possible. You need to be very careful not to break the sting whilst removing it.
Apply an ice pack to the area to help reduce the discomfort and swelling then wash the area with an antiseptic handwash before applying some antiseptic cream. Take an Ibuprofen to help reduce the throbbing pain that accompanies the sting. If the itching persists take an antihistamine and ensure you do not scratch the affected area.
If you develop an allergic reaction you need to consult a doctor. The medication required will depend on the severity of the allergic reaction. Mild to moderate allergic reactions such as rashes and mild breathing problems are treated with antihistamines, steroids, and/or epinephrine injections, and a tetanus booster immunization (if needed). Severe reactions can cause anaphylaxis or anaphylactic shock resulting in low blood pressure, respiratory function could get compromised due to bronchospasm, or a circulatory collapse leading to breathing problems. Severe allergic reaction mostly occurs, when the sting enters the blood stream. Treatment in such cases includes injection of antihistamines, steroids, and epinephrine, placement of a breathing tube into the trachea to aid breathing, intravenous fluids, and hospitalisation and close monitoring.
For an end to your wasp nest problem
Book Now